Understanding DNS and Its Role in Internet Security
The Domain Name System (DNS) is often referred to as the 'phonebook of the internet.' It translates human-friendly domain names like 'example.com' into IP addresses that computers use to identify each other on the network. But DNS is more than just a translation service; it plays a crucial role in internet security and online privacy. In this article, we'll explore what DNS is, how it works, and why it's essential for keeping your online activities safe. We'll also delve into tools like NextDNS that can help you block ads and trackers, enhancing your online privacy.
What is DNS?
DNS stands for Domain Name System. It's a hierarchical and decentralized naming system for computers, services, or other resources connected to the internet or a private network. The primary function of DNS is to translate domain names, which are easy for humans to remember, into IP addresses, which are numerical labels assigned to each device connected to a computer network.
For example, when you type 'www.example.com' into your browser, DNS translates this domain name into an IP address like '93.184.216.34,' allowing your computer to connect to the server hosting the website.
How DNS Works
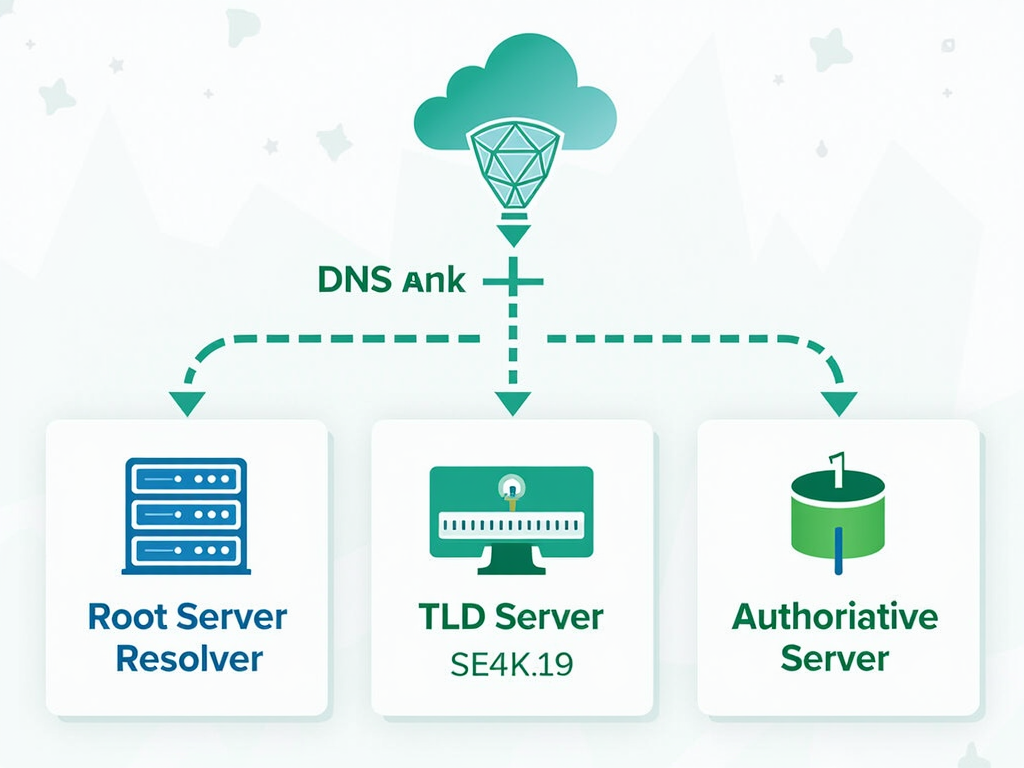
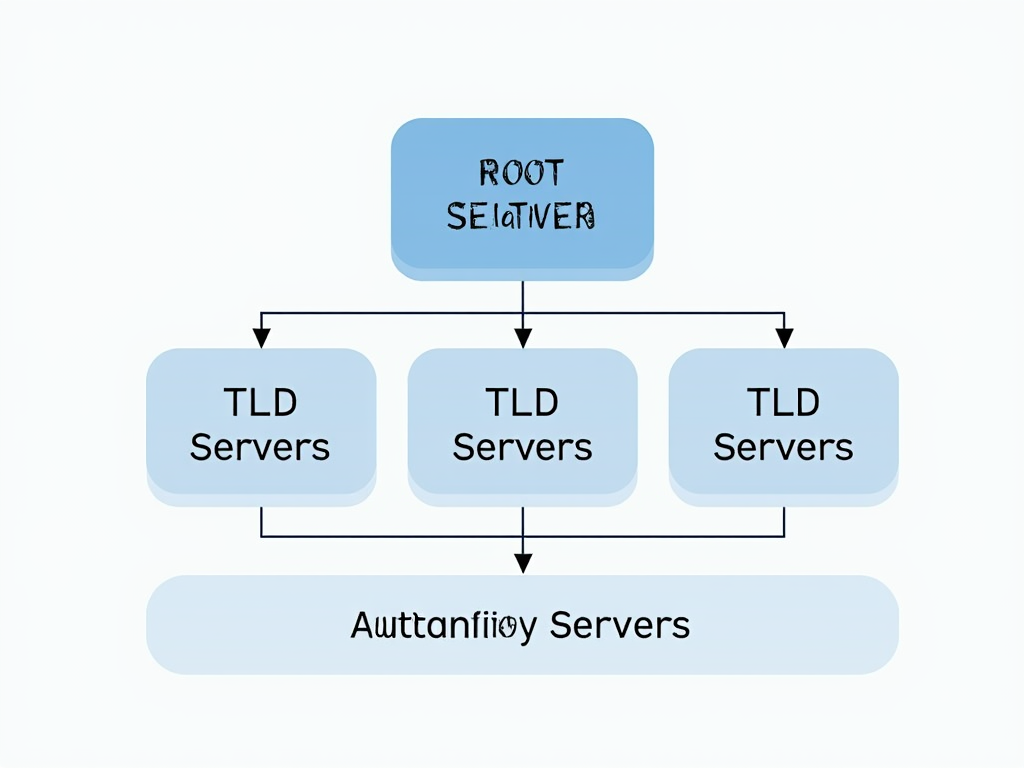
The process of translating a domain name into an IP address is called DNS resolution. Here's a simplified step-by-step explanation of how it works:
- User Request: You enter a domain name into your browser.
- Resolver Query: Your computer sends a query to a DNS resolver, usually provided by your Internet Service Provider (ISP).
- Root Server: The resolver contacts a root server to find out which Top-Level Domain (TLD) server handles the domain's extension (e.g., .com, .org).
- TLD Server: The resolver then queries the appropriate TLD server to find the authoritative server for the domain.
- Authoritative Server: Finally, the resolver asks the authoritative server for the IP address associated with the domain name.
- Response: The resolver sends the IP address back to your computer, which can then connect to the website.
This process happens almost instantaneously, thanks to caching mechanisms that store previously resolved domain names.
DNS and Internet Security
While DNS is essential for internet functionality, it can also be a vector for security threats. Here are some common DNS-related security issues:
- DNS Spoofing: Also known as cache poisoning, this attack involves corrupting the DNS cache with false information, redirecting users to malicious websites.
- DNS Hijacking: Attackers can hijack DNS queries to redirect users to fake websites, often to steal sensitive information.
- DDoS Attacks: Distributed Denial of Service attacks can target DNS servers, overwhelming them with traffic and causing widespread internet outages.
To combat these threats, several security measures have been developed:
- DNSSEC (Domain Name System Security Extensions): This suite of extensions adds an extra layer of security by enabling DNS responses to be digitally signed, ensuring their authenticity.
- Encrypted DNS: Protocols like DNS over HTTPS (DoH) and DNS over TLS (DoT) encrypt DNS queries, preventing eavesdropping and tampering.
Understanding these security measures is crucial for anyone looking to protect their online activities. For more information on DNS security, you can refer to this comprehensive guide by the Internet Society.

NextDNS and Online Privacy Tools
NextDNS is a cloud-based DNS service that offers advanced features for enhancing online privacy and security. It allows users to block ads, trackers, and malicious websites, providing a safer and more private browsing experience. Here's a brief setup guide for using NextDNS to block ads and trackers:
- Create an Account: Sign up for a free account on the NextDNS website.
- Configure Settings: Customize your settings to block ads, trackers, and other unwanted content. You can also set up parental controls and security features.
- Install on Devices: Follow the instructions to configure your devices to use NextDNS. This can be done on individual devices or at the router level for network-wide protection.
- Monitor Activity: Use the NextDNS dashboard to monitor your DNS queries and adjust settings as needed.
In addition to NextDNS, there are other online privacy tools that can be integrated with DNS to enhance security:
- VPNs (Virtual Private Networks): Encrypt your internet connection and mask your IP address.
- Ad Blockers: Prevent ads from loading, reducing exposure to potential malware.
- Privacy-Focused Browsers: Browsers like Brave and Firefox offer built-in privacy features.
For a detailed comparison of online privacy tools, check out this article by the Electronic Frontier Foundation.

Personal Insights and Experiences
As someone who has worked in the tech industry for over a decade, I've seen firsthand how crucial DNS is for both functionality and security on the internet. One memorable experience was when our company's website was targeted by a DNS spoofing attack. Thanks to DNSSEC, we were able to quickly identify and mitigate the threat, preventing any significant damage.
This incident underscored the importance of implementing robust DNS security measures. It's not just about protecting your own data; it's about ensuring the integrity of the entire internet ecosystem. By using tools like NextDNS and staying informed about the latest security practices, you can significantly reduce your risk of falling victim to DNS-related attacks.
In conclusion, DNS is a fundamental component of the internet, translating domain names into IP addresses and enabling seamless navigation. However, its role extends beyond mere translation; it's also a critical element in maintaining internet security and online privacy. By understanding how DNS works and utilizing tools like NextDNS, you can protect yourself from various online threats and enjoy a safer browsing experience.
For those interested in delving deeper into this topic, I recommend the following readings: - 'DNS and BIND' by Cricket Liu and Paul Albitz - 'The Tangled Web: A Guide to Securing Modern Web Applications' by Michal Zalewski - 'Cybersecurity and Cyberwar: What Everyone Needs to Know' by P.W. Singer and Allan Friedman