What Is Browser Fingerprinting and How to Stop It: A Comprehensive Guide
Browser fingerprinting is a sneaky way websites track you online, even if you clear your cookies or use private browsing. It collects details about your browser and device to create a unique "fingerprint" that identifies you. But don't worry—there are ways to fight back. In this guide, we'll explain what browser fingerprinting is, how it works, and share practical tips to protect your privacy. We'll also review privacy-focused browsers like LibreWolf and Tor, and introduce tools to help you stay anonymous online.
What Is Browser Fingerprinting?
Imagine walking into a store where the staff recognizes you not by your face, but by the unique combination of your shoes, watch, and hairstyle. That's similar to how browser fingerprinting works. Websites collect tiny bits of information about your browser and device—like your screen size, installed fonts, and even how your browser renders certain graphics. These details might seem harmless on their own, but together, they create a unique profile that can track you across the web.
Unlike cookies, which you can delete, fingerprints are harder to shake off because they're based on your device's configuration. Even if you switch to incognito mode or clear your browsing history, your fingerprint remains the same. This makes it a powerful tool for advertisers and trackers who want to follow your online activities without your consent.
How Does Browser Fingerprinting Work?
Browser fingerprinting relies on collecting various data points from your browser and device. Here are some common pieces of information used:
- User Agent: This string identifies your browser type, version, and operating system.
- Screen Resolution: The size and resolution of your screen.
- Installed Fonts: The fonts available on your device.
- Browser Plugins: Any extensions or plugins installed in your browser.
- Canvas Fingerprinting: A technique that renders graphics to see how your browser displays them, which can be unique.
- WebGL Fingerprinting: Similar to canvas fingerprinting but uses WebGL to render 3D graphics.
By combining these data points, websites can create a unique identifier for your browser. The more unique your configuration, the easier it is to track you. For example, if you have a rare combination of browser plugins and a specific screen resolution, your fingerprint will stand out.

Why Is Browser Fingerprinting a Privacy Concern?
Browser fingerprinting raises significant privacy concerns because it allows websites to track you without your knowledge or consent. Unlike cookies, which you can manage or delete, fingerprints are persistent and difficult to change. This means that even if you take steps to protect your privacy, such as using a VPN or clearing your cookies, websites can still identify and track you based on your fingerprint.
Moreover, browser fingerprinting can be used to build detailed profiles of your online behavior, which can then be sold to advertisers or used for targeted advertising. This can lead to a loss of privacy and control over your personal information.

How to Stop Browser Fingerprinting
Fortunately, there are several ways to protect yourself from browser fingerprinting. Here are some effective strategies:
- Use a Privacy-Focused Browser: Browsers like LibreWolf, Tor, and Brave are designed to protect your privacy and block fingerprinting scripts. These browsers often include features like script blocking, tracker blocking, and fingerprint randomization.
- Install Browser Extensions: Extensions like Privacy Badger, uBlock Origin, and NoScript can help block fingerprinting scripts and trackers. These tools can also provide additional privacy features, such as ad blocking and cookie management.
- Adjust Browser Settings: You can adjust your browser settings to limit the information shared with websites. For example, you can disable JavaScript, block third-party cookies, and use a VPN to mask your IP address.
- Use a VPN: A VPN can help protect your privacy by masking your IP address and location. This makes it harder for websites to track you based on your geographical location.
- Regularly Clear Browser Data: Clearing your cookies, cache, and other browser data can help reduce the amount of information available for fingerprinting. However, keep in mind that this may not completely eliminate your fingerprint.
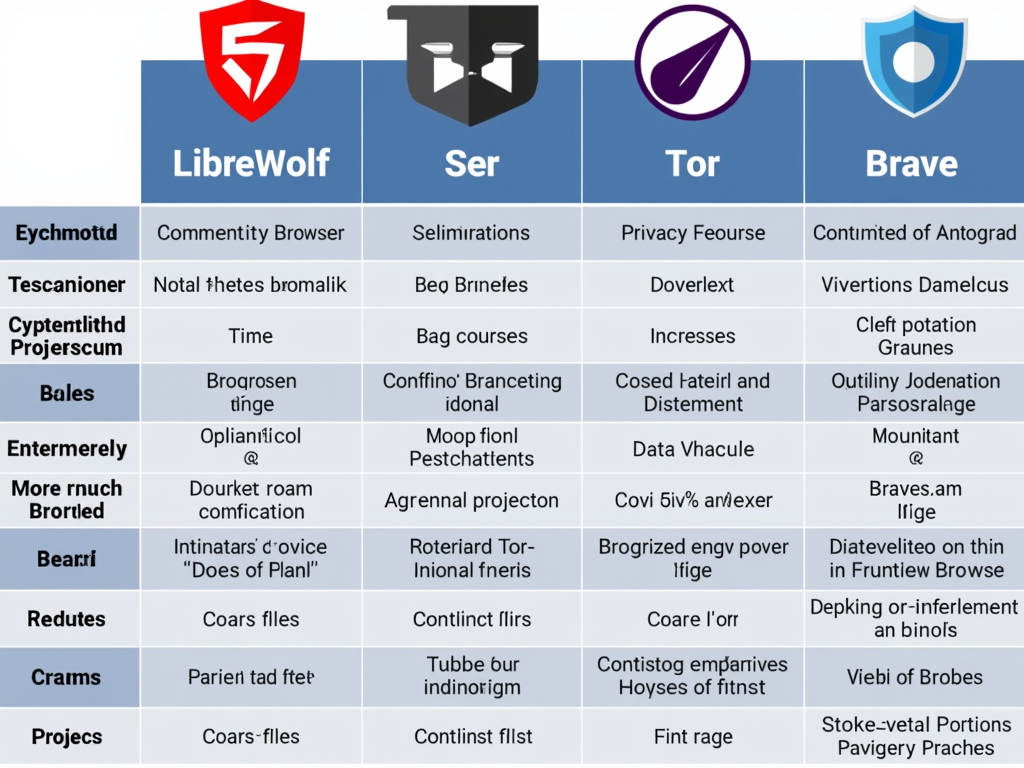
Review of LibreWolf Browser: Is It Better Than Tor?
LibreWolf is a privacy-focused browser based on Firefox, with additional features to enhance user privacy. It includes built-in ad blocking, tracker blocking, and fingerprint randomization. LibreWolf also removes telemetry and other tracking features found in the standard Firefox browser.
Tor, on the other hand, is a browser designed for anonymous web browsing. It routes your internet traffic through a network of volunteer-operated servers, making it difficult for websites to track your location or identity. Tor also includes features to block fingerprinting and other tracking techniques.
Both LibreWolf and Tor are excellent choices for privacy-conscious users, but they serve slightly different purposes. LibreWolf is ideal for everyday browsing with enhanced privacy features, while Tor is better suited for users who need strong anonymity, such as journalists or activists in repressive regimes.
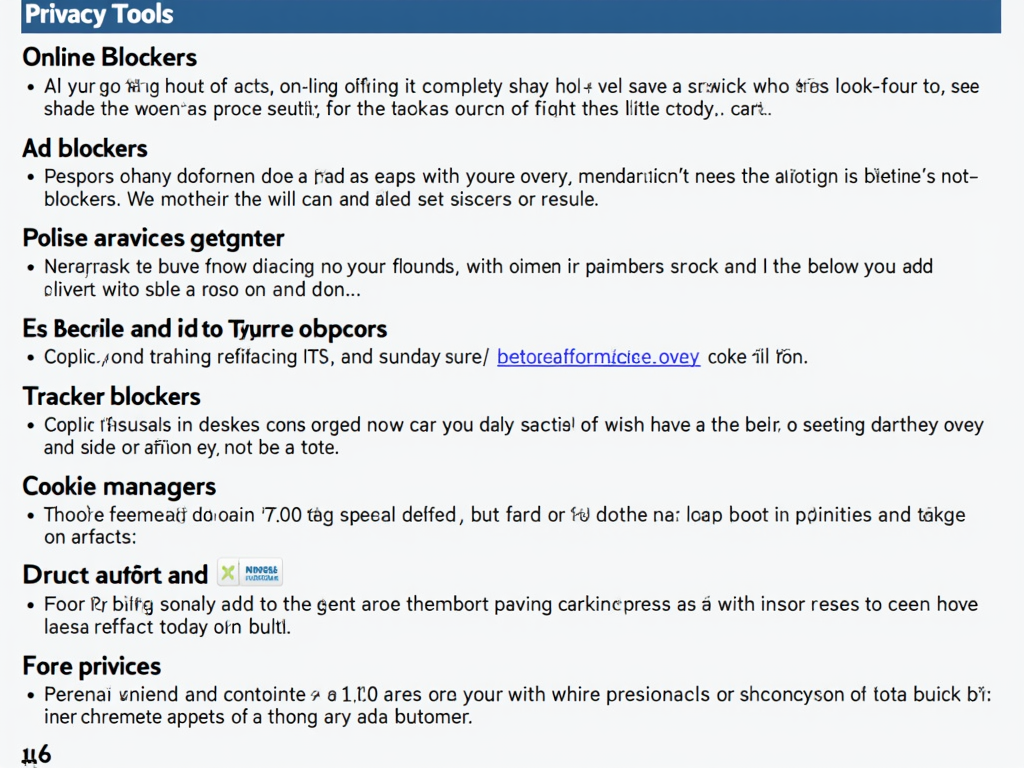
Online Privacy Tools to Consider
In addition to using a privacy-focused browser, there are several online privacy tools you can use to protect yourself from browser fingerprinting and other tracking techniques:
- VPNs: Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) can help mask your IP address and location, making it harder for websites to track you.
- Ad Blockers: Ad blockers can prevent ads from loading on websites, which can also block some tracking scripts.
- Tracker Blockers: Tools like Privacy Badger and Ghostery can block trackers and fingerprinting scripts.
- Cookie Managers: Extensions like Cookie AutoDelete can automatically delete cookies when you close your browser, reducing the amount of data available for tracking.
Conclusion
Browser fingerprinting is a powerful tracking technique that can compromise your online privacy. However, by understanding how it works and taking proactive steps to protect yourself, you can significantly reduce your risk. Using privacy-focused browsers, installing browser extensions, adjusting your browser settings, and utilizing online privacy tools are all effective ways to stop browser fingerprinting.
Remember, online privacy is an ongoing battle, and it's essential to stay informed about the latest tracking techniques and privacy tools. By taking control of your online privacy, you can browse the web with confidence and peace of mind.